iPosture? Are Phones/Tablet Computers Causing Neck and Shoulder Pain?
 Whether you’re an Apple fan, an Android lover or a hardcore Microsoft user, there’s no denying the popularity of tablet computers. The numbers speak for themselves—technology market analysts estimate that over 200 million of them are sold in the US each year. Even if you don’t follow the latest tech trends, you know that mobile devices—principally phones and tablets—are a regular feature around town. From coffee shops and supermarkets to airports and train platforms, they seem to be everywhere. Plus a growing number of businesses are beginning to equip their sales and service staff as well as their executive teams with them. They’re even finding their way into hospitals and doctor’s offices!
Whether you’re an Apple fan, an Android lover or a hardcore Microsoft user, there’s no denying the popularity of tablet computers. The numbers speak for themselves—technology market analysts estimate that over 200 million of them are sold in the US each year. Even if you don’t follow the latest tech trends, you know that mobile devices—principally phones and tablets—are a regular feature around town. From coffee shops and supermarkets to airports and train platforms, they seem to be everywhere. Plus a growing number of businesses are beginning to equip their sales and service staff as well as their executive teams with them. They’re even finding their way into hospitals and doctor’s offices!
But while tablets certainly have their benefits, new research suggests that they also have their drawbacks when it comes to musculoskeletal health. It has already been shown that frequent texting on your mobile phone can cause problems with neck pain (the so-called “text neck” epidemic), but those who use their tablet for everything from work-related applications to just surfing the internet and watching full-length movies may be in for even more pain. The anecdotal evidence is already starting to show up in the waiting rooms of chiropractic offices around the country, and researchers at leading universities are beginning to seriously study the ergonomics and health risks of tablet use.
The results of a study published in Work: A Journal of Prevention, Assessment, and Rehabilitation found that the use of tablet computers was associated with greater head and neck flexion than traditional desktop computers and that placing the tablet higher on a table and using a case to put the tablet at a more optimal angle could help prevent neck and shoulder problems.
Researchers from the Harvard School of Public Health, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Microsoft Corporation studied 15 volunteers who were regular users of tablet computers. The subjects performed simulated tasks on an Apple iPad2 and a Motorola Xoom, during which the posture of the head and neck, the subjects’ gaze angle and gaze distance were measured by a three-dimensional infrared motion analysis system. They surfed the internet, wrote e-mails, watched movies and played video games.
Each tablet came with its own proprietary case that enabled users to set the tablet at different angles. The Apple case allowed for 15° and 73° tilt angles, while the Motorola case allowed angles of 45° and 63°. Greater flexion of the neck was found with the iPad2 when used in its case. Not surprisingly, tablets set at the least perpendicular angle caused greater neck and head flexion than when the subjects used a desktop or laptop computer. Head and neck posture only began to approach a neutral position when the tablets were set in their cases at the Table-Movie angle at which they were closest to perpendicular.
The researchers recommended that tablet users place the devices on a table and at the steepest viewing angle possible to avoid neck and shoulder pain. However, they cautioned that this configuration might cause problems for the arms and wrists, which in this configuration are not optimally placed for input. This of course can lead to its own set of musculoskeletal problems in the extremities. So the simple fact of the matter is that tablet ergonomics involve some tough compromises or trade offs for users. A position that’s ideal for viewing is troublesome for typing and gestures and vice-versa.
For many people, tablet computers have become an indispensable part of work and home life (for better or for worse). If you’re one of these people and can’t conceive of either giving up your iPad or reducing the number of hours you spend using it, then it’s very important to develop good ergonomic habits that minimize musculoskeletal stress and have the smallest impact on your posture. You should also consider seeing your chiropractor on a regular basis. Chiropractic care has been shown to be more effective in treating neck and shoulder pain than using pain medication. A chiropractic adjustment can realign neck vertebrae and take the pressure off compressed nerves, bringing relief in a gentle, natural manner and allowing you to use your tablet more comfortably. In addition to addressing the problems you already have, your chiropractor will also be able to offer specific ergonomic advice to help prevent them from recurring or becoming chronic.
Contact Southeastern Healthcare for Neck Pain Relief!
We’re here to help! Whether you have specific concerns about a musculoskeletal problem or more general health and wellness questions, we encourage you to call or visit our office today!
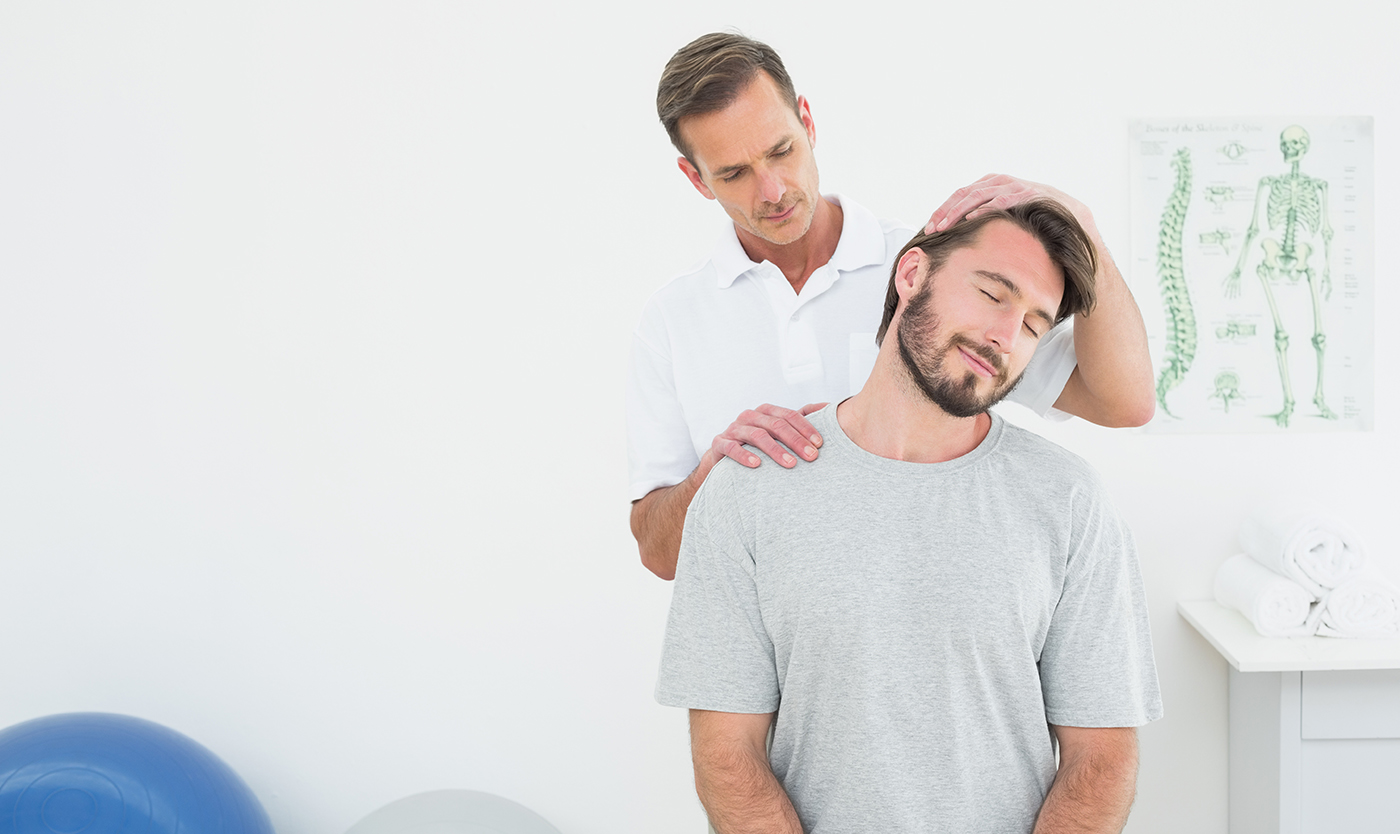


 Have you ever felt an uncomfortable tingling sensation in your arm after performing the same motion for an extended period of time? Maybe it was after spending a day typing at your computer or raking leaves. This sensation may be caused by nerve entrapment syndrome, a common condition that is sometimes referred to as either a “trapped nerve” or a “pinched nerve”.
Have you ever felt an uncomfortable tingling sensation in your arm after performing the same motion for an extended period of time? Maybe it was after spending a day typing at your computer or raking leaves. This sensation may be caused by nerve entrapment syndrome, a common condition that is sometimes referred to as either a “trapped nerve” or a “pinched nerve”.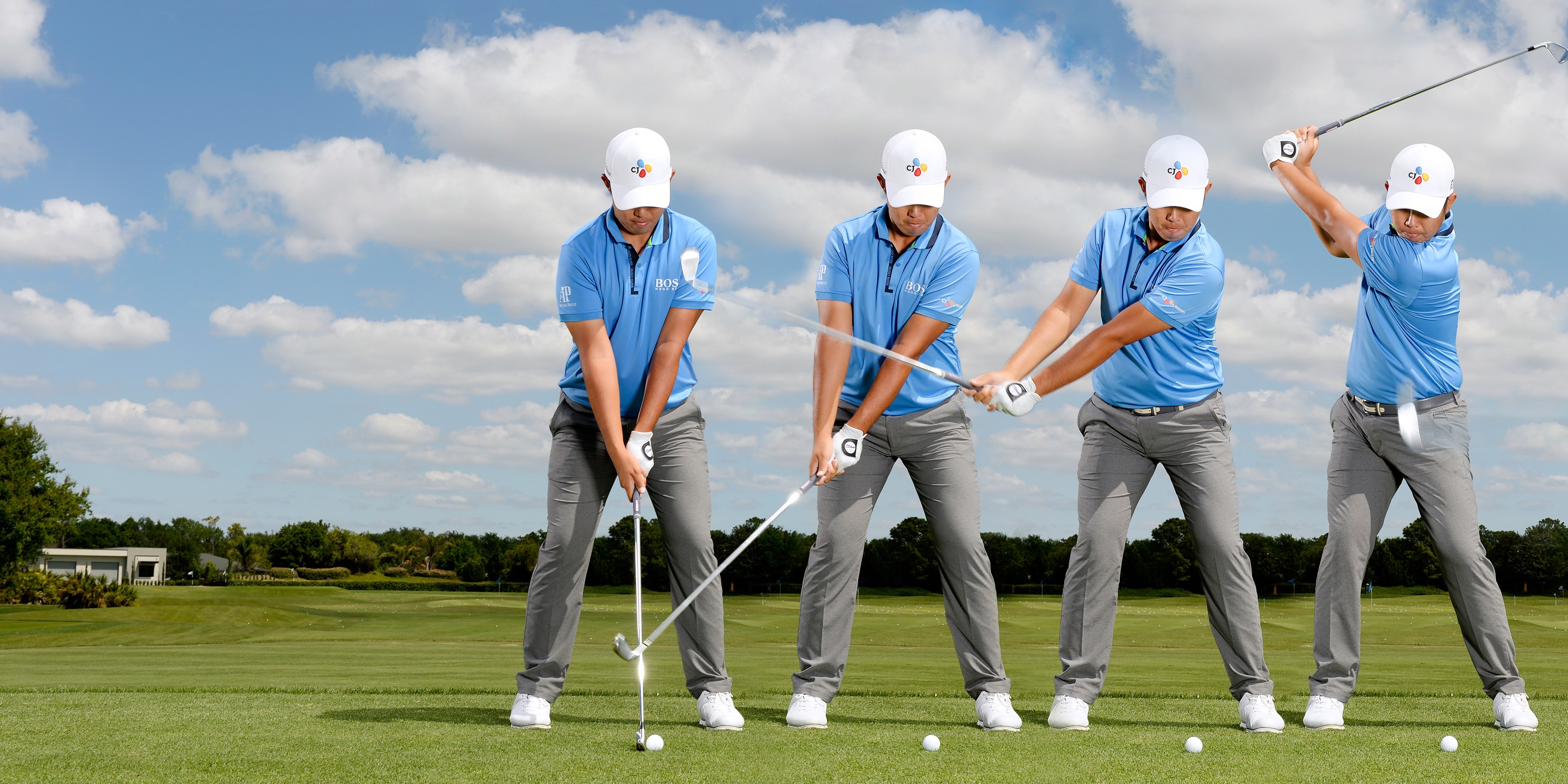  If you don’t know better, golf can seem like a laid-back sport that carries little risk of physical injury other than being hit by a stray ball or having a foot run over by a speeding golf cart. But the truth is that a correct golf swing requires a great deal of balance, flexibility and core strength and that it can place a great deal of strain on the golfer’s back.
If you don’t know better, golf can seem like a laid-back sport that carries little risk of physical injury other than being hit by a stray ball or having a foot run over by a speeding golf cart. But the truth is that a correct golf swing requires a great deal of balance, flexibility and core strength and that it can place a great deal of strain on the golfer’s back. Unless you’re either very, very young or live on a remote desert island without TV, radio, Internet or print media, you’ve probably heard the term “core strength” before. Serious athletes and exercise enthusiasts talk about it at the fitness center, and so do their coaches and trainers. But did you know that chiropractors and physical therapists talk about it too? So what exactly is core strength and why do some kinds of healthcare professionals care about it so much?
Unless you’re either very, very young or live on a remote desert island without TV, radio, Internet or print media, you’ve probably heard the term “core strength” before. Serious athletes and exercise enthusiasts talk about it at the fitness center, and so do their coaches and trainers. But did you know that chiropractors and physical therapists talk about it too? So what exactly is core strength and why do some kinds of healthcare professionals care about it so much?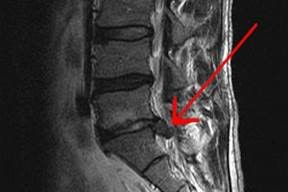 One of the most common causes of lower back pain occurs when the spinal disks in the lumbar area become herniated. A herniated disk happens when the bone of the disk itself has crumbled or fractured and the soft inner core bulges out through the outer portion of the disk. This places pressure on the spinal nerve root that runs through the disks, and the result can be pain in the lower back as well as numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs and buttocks. Medical doctors tend to treat acutely herniated disks with oral steroids and epidural injections of cortisone, both of which have limited success rates and adverse side effects.
One of the most common causes of lower back pain occurs when the spinal disks in the lumbar area become herniated. A herniated disk happens when the bone of the disk itself has crumbled or fractured and the soft inner core bulges out through the outer portion of the disk. This places pressure on the spinal nerve root that runs through the disks, and the result can be pain in the lower back as well as numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs and buttocks. Medical doctors tend to treat acutely herniated disks with oral steroids and epidural injections of cortisone, both of which have limited success rates and adverse side effects.
 Many people are under the mistaken impression that the head-sized extension at the top of your car’s seat is a head rest. It’s actually not a place to rest your weary head during a long drive, but rather a safety feature called a head restraint that is there to help prevent whiplash in the event of a rear-end collision. And having it adjusted properly can mean the difference between emerging unscathed and enduring weeks of neck pain, along with the cost and inconvenience of medical treatment.
Many people are under the mistaken impression that the head-sized extension at the top of your car’s seat is a head rest. It’s actually not a place to rest your weary head during a long drive, but rather a safety feature called a head restraint that is there to help prevent whiplash in the event of a rear-end collision. And having it adjusted properly can mean the difference between emerging unscathed and enduring weeks of neck pain, along with the cost and inconvenience of medical treatment.